About NICU
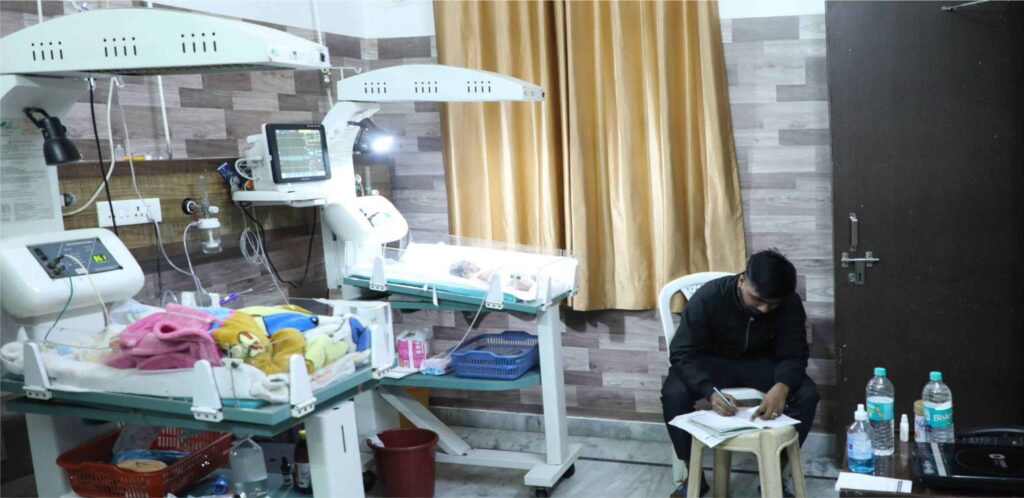
About Instruments and NICU
Instruments
Sanjiv Singla Children Hospital is equipped with state-of-the-art medical instruments to ensure the highest quality of care for pediatric and neonatal patients. Our focus is on precision, innovation, and reliability in every aspect of patient care. The hospital regularly upgrades its equipment to incorporate the latest advancements in medical technology.
Key Instruments Include:
- Neonatal Incubators: Provide controlled temperature and humidity for premature and critically ill newborns.
- Open Warmers: Ensure consistent thermal support for infants requiring stabilization.
- Ventilators and CPAP Machines: Deliver respiratory support for infants with breathing difficulties.
- Infusion Pumps: For accurate administration of medications and fluids.
- Multi-Parameter Monitors: Track vital signs such as heart rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure.
- Phototherapy Units: Treat neonatal jaundice effectively.
- Syringe Pump: Designed to handle small and precise amounts of medication required for infants
NICU (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit)
The NICU at Sanjiv Singla Children Hospital is a 24-bedded, advanced care unit designed to cater to the critical needs of newborns and preterm babies. It is staffed by experienced neonatologists and trained nurses who provide round-the-clock care.
NICU Highlights:
- Advanced respiratory support with centralized oxygen supply.
- Comprehensive monitoring systems for real-time assessment.
- Specialized care for conditions such as prematurity, low birth weight, congenital abnormalities, and sepsis.
- Family-centered care approach to support parents during challenging times.
- Nutritional rehabilitation programs for the long-term well-being of newborns.
At Sanjiv Singla Children Hospital, we prioritize creating a child-friendly environment to ensure the comfort and recovery of every patient.
Comprehensive List of Neonatal Diseases
Here is a detailed overview of neonatal diseases, categorized for clarity:
1. Respiratory Disorders
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
- Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTN)
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS)
- Apnea of Prematurity
- Pneumonia
2. Infectious Diseases
- Neonatal Sepsis
- Congenital Infections (TORCH)
- Toxoplasmosis
- Other (Syphilis, Varicella, Parvovirus)
- Rubella
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)
- Meningitis
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
3. Jaundice and Liver Disorders
- Physiological Jaundice
- Pathological Jaundice
- Biliary Atresia
- Neonatal Hepatitis
4. Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders
- Hypoglycemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Congenital Hypothyroidism
- Inborn Errors of Metabolism (e.g., Phenylketonuria, Galactosemia)
5. Neurological Disorders
- Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
- Intracranial Hemorrhage (ICH)
- Seizures
- Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS)
6. Gastrointestinal Disorders
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Congenital Anomalies (e.g., Esophageal Atresia, Gastroschisis)
- Meconium Ileus
7. Cardiovascular Disorders
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
- Congenital Heart Defects (e.g., Tetralogy of Fallot, VSD, ASD)
- Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn (PPHN)
8. Hematological Disorders
- Anemia of Prematurity
- Neonatal Polycythemia
- Hemorrhagic Disease of the Newborn
- Blood Group Incompatibility (Rh and ABO)
9. Genetic and Congenital Anomalies
- Down Syndrome
- Cleft Lip and Palate
- Neural Tube Defects (e.g., Spina Bifida, Anencephaly)
- Cystic Fibrosis
10. Skin and Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Birth Injuries (e.g., Cephalohematoma, Fractures)
- Neonatal Rashes (e.g., Erythema Toxicum, Milia)
- Clubfoot (Talipes Equinovarus)
11. Eye and Ear Conditions
- Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
- Congenital Cataracts
- Hearing Loss
12. Immune Disorders
- Neonatal Lupus
- Immune Deficiency Syndromes
13. Prematurity-Related Complications
- Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD)
- Feeding Difficulties
- Temperature Instability
14. Other Disorders
- Birth Asphyxia
- Umbilical Infections (Omphalitis)
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
Conclusion
Each neonatal condition requires specialized care, often involving advanced diagnostics, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) facilities, and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment and rehabilitation.
Common Diseases in Neonates
Neonates, or newborns, are susceptible to various diseases due to their underdeveloped immune systems and physiological immaturity. Early detection and treatment are critical to ensuring their survival and health. Here are some common neonatal diseases:
1. Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS)
- Cause: Immature lungs and lack of surfactant.
- Symptoms: Rapid breathing, grunting, flaring nostrils, and cyanosis.
- Treatment: Oxygen therapy, surfactant replacement, and mechanical ventilation if needed.
2. Neonatal Jaundice
- Cause: High bilirubin levels due to immature liver.
- Symptoms: Yellowing of skin and eyes.
- Treatment: Phototherapy and, in severe cases, exchange transfusion.
3. Neonatal Sepsis
- Cause: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections.
- Symptoms: Lethargy, poor feeding, fever, or hypothermia.
- Treatment: Broad-spectrum antibiotics and supportive care.
4. Hypoglycemia
- Cause: Low blood sugar due to prematurity, maternal diabetes, or delayed feeding.
- Symptoms: Jitteriness, poor feeding, seizures, and apnea.
- Treatment: IV glucose administration and frequent feeding.
5. Prematurity-Related Complications
- Common Issues: Underdeveloped organs, feeding difficulties, and increased risk of infections.
- Management: NICU support with respiratory aids, nutritional care, and monitoring.
6. Birth Asphyxia
- Cause: Lack of oxygen during birth.
- Symptoms: Difficulty breathing, low heart rate, and weak muscle tone.
- Treatment: Resuscitation, ventilation, and cooling therapy to prevent brain damage.
7. Congenital Abnormalities
- Examples: Heart defects, cleft palate, and neural tube defects.
- Management: Surgical interventions, NICU care, and long-term monitoring.
8. Neonatal Infections
- Examples: Pneumonia, meningitis, and urinary tract infections.
- Management: Antibiotics, antifungals, or antivirals, along with supportive care.
9. Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS)
- Cause: Inhalation of meconium-stained amniotic fluid.
- Symptoms: Difficulty breathing, cyanosis, and rapid heart rate.
- Treatment: Suctioning, oxygen therapy, and mechanical ventilation.
10. Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC)
- Cause: Inflammation and damage to the intestines, often in premature infants.
- Symptoms: Abdominal distension, feeding intolerance, and blood in stools.
- Treatment: Antibiotics, bowel rest, and surgery if necessary.
Prevention and Care
- Antenatal Care: Proper maternal health and nutrition during pregnancy.
- Hygiene: Strict infection control measures in the NICU.
- Breastfeeding: Strengthens immunity and promotes healthy growth.
- Immunization: Protects against preventable diseases.
Early diagnosis, advanced NICU care, and a multidisciplinary approach are essential for the successful treatment and recovery of neonates with these conditions.


